The world of automation and mechanical systems has been revolutionized by the power of air. Pneumatics, derived from the Greek word meaning air or wind, represents the science and technology of using compressed air to perform mechanical work. This dynamic field has shaped modern industries by delivering clean, efficient, and reliable energy to power various applications. Understanding the true pneumatic definition opens the door to appreciating how air-powered mechanisms enhance productivity, precision, and performance.
Understanding The Core Of Pneumatic Technology
At its essence, pneumatic is about harnessing the potential of compressed air to create motion or force. By converting energy stored in compressed air into mechanical movement, pneumatic systems offer a safe and efficient alternative to electrical or hydraulic systems.
Key characteristics of pneumatic systems include:
- Clean and environmentally friendly operation, using air as the working medium.
- High speed and responsiveness, ideal for automated applications.
- Reliable performance, with minimal maintenance requirements.
- Safe operation, as air poses no risk of combustion or contamination.
These attributes make pneumatics an essential technology in industries that prioritize efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
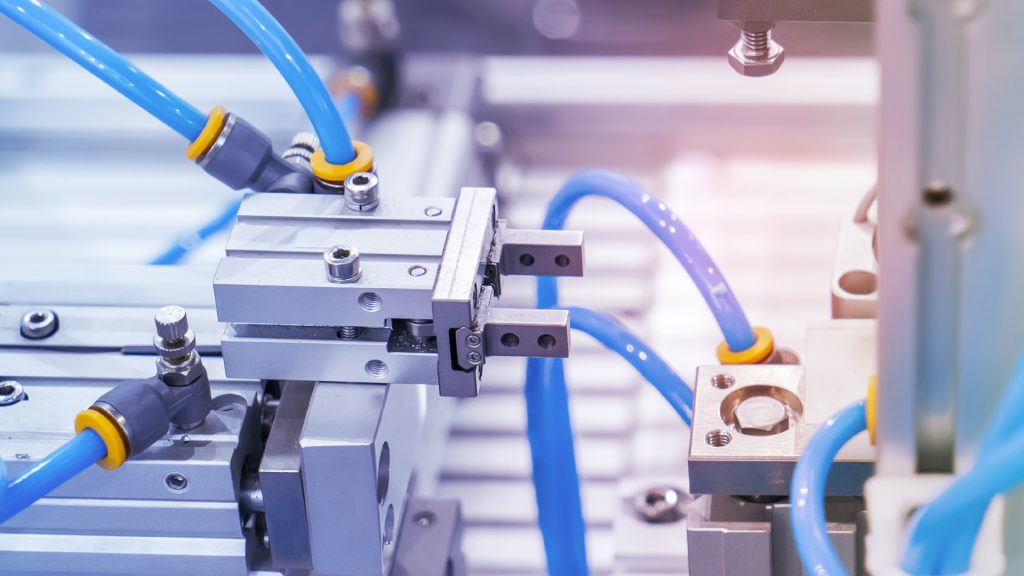
How Air-Powered Mechanisms Work
A pneumatic system typically consists of several main components that work together to generate motion. The process begins with the compression of air, which is then stored and controlled through various devices to produce mechanical output.
Main components include:
- Compressor: Generates and stores compressed air.
- Valves: Control airflow and regulate pressure within the system.
- Actuators and Cylinders: Convert air pressure into linear or rotary motion.
- Air treatment units: Ensure clean, dry air for optimal system performance.
Through this well-coordinated process, air-powered mechanisms deliver precise control and efficient energy conversion, powering tools, machines, and automation systems across countless applications.
Advantages Of Pneumatic Systems In Modern Applications
Pneumatic technology continues to grow in relevance due to its adaptability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. From manufacturing to robotics, air-powered systems bring dependable performance and flexible design options.
Key advantages include:
- Energy efficiency, utilizing renewable and easily available compressed air.
- Simplified design, leading to faster installation and lower costs.
- Durability, even under demanding operating conditions.
- High operational speed, perfect for automation and repetitive tasks.
These benefits contribute to consistent productivity and reduced downtime, helping industries operate smoothly and efficiently.
Sustainability And The Future Of Pneumatics
Modern pneumatic definition systems are increasingly designed with sustainability in mind. Innovations in energy recovery, low-leakage components, and smart sensors are helping reduce energy consumption while maintaining high performance.
Positive sustainability trends include:
- Optimized airflow management to minimize waste.
- Integration with digital monitoring systems for improved efficiency.
- Use of recyclable materials, aligning with eco-friendly goals.
By combining innovation with environmental responsibility, pneumatic technology continues to evolve as a cornerstone of sustainable industrial progress.
Conclusion: Embracing The Power Of Air
Exploring the true pneumatic definition reveals more than just a science of air it represents a movement toward smarter, safer, and more efficient mechanical systems. Air-powered mechanisms embody innovation through simplicity, offering clean energy solutions that keep industries moving forward. As technology advances, pneumatics will remain a key driver in shaping a future defined by sustainability, reliability, and precision performance.

